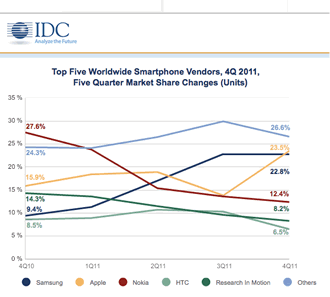
A report from Patrick Moorhead’s Moor Insights & Strategy has asserted that, although the server market is dominated by Dell, HP and IBM at present, Lenovo is well positioned to break out of the “other” category and start making a serious dent in market share.
A report from Patrick Moorhead’s Moor Insights & Strategy has asserted that, although the server market is dominated by Dell, HP and IBM at present, Lenovo is well positioned to break out of the “other” category and start making a serious dent in market share.
Players like Cisco and Fujitsu, 4th and 5th in the server market respectively, could even be overtaken by Lenovo in the near future. But it has some hurdles to leap and if it is to do so, Lenovo will have to prioritise servers.
Looking at Lenovo’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT), it’s clear the company can compete on price and has a robust supply chain behind it. The company is leading in the growing China market, performing well with SMBs, and there remains a perceived tie with IBM when Big Blue sold off a chunk of its hardware.
However, Lenovo doesn’t offer cloud services or a complete product line outside of its home turf and is somewhat lacking on the ineternational enterprise stage. It has no small core direction, according to Moor Insights, a weak storage offering, and no apparent network switch or fabric offering.
Moor Insights & Strategy believes Lenovo will have the opportunity, although not without challenges, to pick up IBM’s x86 server business, which could address some of the above concerns. There is also a window for Lenovo to expand its SMB offerings within EMEA, particularly western Europe, where small to medium businesses are highly concentrated.
If Lenovo decided to buy IBM’s x86 business, Moor thinks it’s likely it’d go for the whole lot, while IBM could minimise damage to its own bottom line by maintaining blade IP, which it could then license to Lenovo. An acquisition would propel Lenovo to #3 in the server charts, way ahead of Fujitsu and Cisco, but the buy would have to be twinned with serious efforts to maintain previous IBM customers to prevent seduction over to rivals like HP or Dell.
Moor Insights suggests Lenovo focus on the cloud, where it is underrepresented, as well as building a portfolio it can extend to the large business market. It must also underline its “message” – although it’s understood Lenovo performs well in client devices, the message is “not translating in the server market,” according to Moor. Lenovo needs to reinforce its position to potential enterprise customers.
Lenovo, the report says, is “at an interesting crossroads in the server market”. While there is ample opportunity for the company to really cement its position and overtake some of the competition, it will need to invest heavily.
“Lenovo has an opportunity to break out of its position and quickly move up in the market, as well it remains a company that could disrupt the market the way that Dell did years ago. But in order to do that, it needs to get into the market in a serious way,” the report concludes.
 Dell has rolled out a new Dell Precision mobile workstation and it’s a very interesting piece of kit. Dell claims the new M3800 is the world’s lightest and thinnest workstation, which is hard to dispute as it weighs in at just 4.15 pounds and it’s a mere 18mm thick.
Dell has rolled out a new Dell Precision mobile workstation and it’s a very interesting piece of kit. Dell claims the new M3800 is the world’s lightest and thinnest workstation, which is hard to dispute as it weighs in at just 4.15 pounds and it’s a mere 18mm thick.