According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the British economy shrank 0.3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2012, reflecting wider economic woes in the Eurozone and further afield.
According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the British economy shrank 0.3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2012, reflecting wider economic woes in the Eurozone and further afield.
The figures were lower than expected for the last three months of 2012 and have sparked fears that, if the economy does not pick up, the UK will enter an unprecedented ‘triple dip recession’ – although arguably, Britain never left the recession at all. Chancellor George Osborne has warned that tough times still lie ahead for the country, but shirked advice from the International Monetary Fund that he and the Coalition should ease up on the policy of austerity.
On the GDP figures, Osborne said: “We have a reminder today that Britain faces a very difficult economic situation”.
The figures serve as a “reminder that last year was particularly difficult” and that the country faces problems at home “because of the debts built up over many years and problems abroad with the Eurozone, where we export most of our products, in recession”. The opposition accused Osborne and Prime Minister David Cameron of being “asleep at the wheel”, although the macroeconomic environment is unrelentingly difficult and both Labour and Conservatives differ on many minutae of policy – with the wider climate beyond their control.
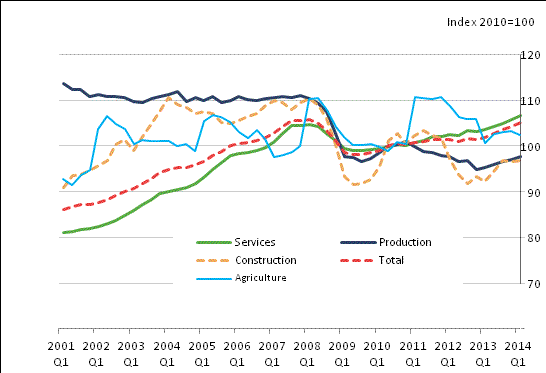
GDP, meanwhile, was flat compared to the same time last year. Production output decreased by 1.8 percent for the quarter, negating a 0.7 percent increase between the second and third quarters. Service industry output was flat from Q3 into Q4, although that followed a 1.2 percent boost between Q2 and Q3 2012.
Britain enjoyed steady GDP growth from 2000 right up until the world markets crashed in 2008, and according to the ONS, the decline of economic conditions in 2008 and up until now has had a significant effect on construction and production – though the service sector wasn’t hit as hard, and is now slowly returning to 2008 levels.
In October last year, channel analyst house Canalys’ CEO, Steve Brazier, said that, despite the difficult economic climate, there is still opportunity in the channel. Although growth was not exactly meteoric, Brazier said that by carefully steering the ship, channel players could weather the storm, although the market will be tough.
Senior analyst at Canalys, Rachel Brindley, offered some thoughts to ChannelEye on just what channel players can do to push through the crisis. She tells us the situation isn’t exactly all doom and gloom.
“Some partners will struggle if this economy goes into a triple dip recession,” Brindley said, “but there is a chance that it could happen. That being said, a lot are well placed – those who focus on customer service, keeping existing customers very close, growing their services business an diversifying their portfolio into things like managed services and data centres, will rise to the difficult times we’ve been going through”.
“Generally,” Brindley said, “those that focus on their customers, and diversify their business away from traditional hardware and box shifting will come through OK, it will come down to careful planning and taking opportunities in spaces like the data centre and looking at what’s going on in the networking space”.
 The Office for National Statistics (ONS) said that UK gross domestic product (GDP) rose by 0.8 percent in the first calendar quarter of this year.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) said that UK gross domestic product (GDP) rose by 0.8 percent in the first calendar quarter of this year.