The Gartner Group has studied the tea leaves at the bottom of its tea cup and come up with some predictions on the future of wearable devices.
The Gartner Group has studied the tea leaves at the bottom of its tea cup and come up with some predictions on the future of wearable devices.
The market research company predicts that by 2017, a third of so-called “smart wearables” will be practically invisible.
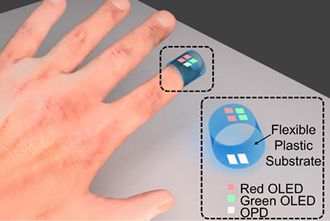
Gartner said smart contact lenses are already being developed, and there’s some interesting projects creating smart jewellery. Why would you need smart jewellery? They could deliver comms alerts and emergency alarms, according to Annette Zimmermann, research director at Gartner.
These will be in contrast to smart glasses, which are pretty easy to spot.
And we’ll also see the proliferation of head mounted displays (HMDs) for virtual reality but they’ll have to be not only smart, but smart looking.
Gartner also predicts that by 2016, 40 percent of smartphones will include biometric sensors with such features as fingerprint, facial, iris, voice and palm vein authentication.
And Gartner sees the end of Windows. It estimates that in 2017. a third of people in emerging markets will never have owned a Windows device.